How to select heat exchange tubesheet?
How to Selecte Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets?
1. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Material Selection
Carbon Steel: Suitable for non-corrosive environments and low to medium temperature and pressure applications. It is cost-effective but has limited corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel: Offers good corrosion resistance and is suitable for corrosive media and higher temperature environments. Common grades include 304 and 316.
Copper Alloys: Such as brass and copper-nickel alloys, are suitable for seawater or other highly corrosive media.
Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys: Lightweight and good thermal conductivity, but generally less corrosion-resistant, suitable for specific applications.
Special Alloys: Such as titanium alloys and nickel-based alloys, suitable for extreme corrosive environments but are expensive.
2. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Thickness Selection
Calculation Method: The thickness is calculated based on working pressure (P), allowable stress of the tube sheet material (S), tube hole diameter (d), and corrosion allowance (C). A commonly used formula is:
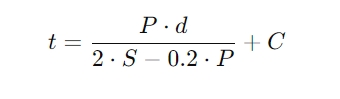
where t is the tube sheet thickness.
Reference Standards: Use standards like ASME and GB for specific calculations to ensure compliance with regulations.
3. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Hole Diameter and Pitch Design
Hole Diameter: Typically 0.2-0.5 mm larger than the outer diameter of the heat exchanger tube to facilitate assembly and welding.
Pitch: Designed based on the type of heat exchanger and fluid properties. Generally, the center distance of holes is 1.25-1.5 times the outer diameter of the heat exchanger tube to ensure fluid flow and heat exchange efficiency.
4. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Machining Precision
Drilling Accuracy: High-precision heat exchangers require CNC drilling or boring machines to ensure the accuracy of hole diameters and pitches.
Flatness and Perpendicularity: The flatness of the tube sheet and the perpendicularity of the holes should be within specified ranges to ensure the installation accuracy of the heat exchanger tubes.
5. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Welding and Sealing
Welding Process: Choose an appropriate welding method such as TIG welding, MIG welding, or manual welding. Perform welding procedure qualification (WPS/PQR) before welding to ensure welding quality.
Sealing Performance: For heat exchangers requiring high sealing performance, a combination of expansion and welding for double sealing can be used.
6. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Inspection and Maintenance
Removable Design: Consider the removability of the tube sheet in the design for easy cleaning, inspection, and replacement of heat exchanger tubes.
Maintenance Space: Leave enough maintenance space to ensure easy disassembly and assembly of tube bundles and tube sheets during maintenance.
7. Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Standards and Specifications
ASME VIII: American Society of Mechanical Engineers Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
TEMA: Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association standards.
GB 151: Chinese National Standard for Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers.
Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets Example Analysis
Suppose we need to design a shell-and-tube heat exchanger for the chemical industry with corrosive liquid as the medium, working pressure of 2 MPa, working temperature of 200°C, and heat exchanger tube outer diameter of 25 mm.
1. Material Selection: Choose 316 stainless steel due to the corrosive nature of the medium.
2. Thickness Calculation: Assuming the allowable stress for 316 stainless steel is 150 MPa and corrosion allowance is 2 mm, the calculation is:
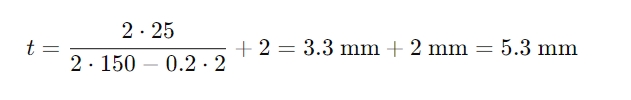
For safety, choose a tube sheet thickness of 6 mm.
3. Hole Diameter and Pitch: Hole diameter is 25.5 mm, and the center distance of holes is 31.25 mm.
4. Machining Precision: Use CNC drilling machines to ensure hole diameter tolerance of ±0.1 mm and pitch tolerance of ±0.2 mm.
5. Welding and Sealing: Use TIG welding and perform welding procedure qualification to ensure welding quality.
6. Inspection and Maintenance: Design a removable tube sheet with enough maintenance space for easy cleaning and replacement of tube bundles.
7. Standards and Specifications: Follow ASME VIII and TEMA standards throughout the design and manufacturing process.


