Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters (LP Feedwater Heaters)
2024-06-09Leave a message
Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters (LP Feedwater Heaters)
1. What are Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters?
Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters (LP Feedwater Heaters) are heat exchangers used in power generation and industrial boiler systems. They preheat the feedwater entering the boiler using steam extracted from the steam turbine. This preheating process improves the overall efficiency of the boiler system by reducing the amount of fuel needed to heat the water to the required temperature.
2. Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters Main Functions
- Improve Thermal Efficiency: Preheating the feedwater reduces the fuel required by the boiler, thus increasing its efficiency.
- Reduce Thermal Stress: Lowering thermal stress on the boiler and pipes extends the equipments lifespan.
- Save Fuel: Reduces fuel consumption, lowering operational costs.
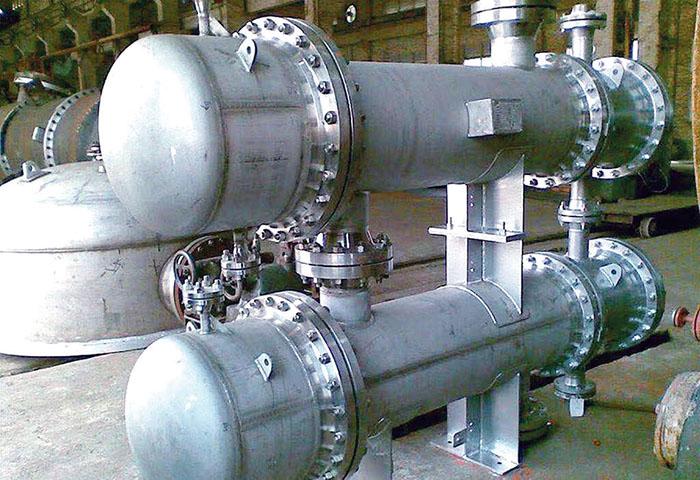
3. LP Feedwater Heaters Structure and Components
- Heating Tube Bundle: Typically made of carbon steel, stainless steel, or copper-nickel alloy, often designed with finned tubes or extra long U bend tube to increase the heat transfer surface area.
- Shell: Cylindrical structure, usually made of carbon steel or stainless steel, ensuring good sealing and pressure resistance.
- End Covers: Seal both ends of the shell and are equipped with inlet and outlet pipe connections, facilitating maintenance and cleaning.
- Tube Sheets: Secure the heating tube bundle and separate the steam and water, ensuring heat exchange occurs in an enclosed environment.
- Drainage System: Includes drain valves and drain pipes to remove condensate, preventing water accumulation from affecting heat transfer efficiency.
4. LP Feedwater Heaters Working Principle
- Steam Entry: Steam extracted from the steam turbine enters the heater through pipes and flows along the outside of the heating tube bundle.
- Heat Exchange: The heat from the steam is transferred through the walls of the heating tubes to the feedwater inside, raising the feedwater temperature while the steam condenses into water.
- Condensate Discharge: Condensate is discharged through the drainage system, ensuring no water accumulation inside.
- Heated Feedwater: Preheated feedwater continues to flow to the boiler, enhancing the overall thermal efficiency by entering the boiler at a higher temperature.
5. Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters Applications
- Thermal Power Plants: Improves boiler efficiency, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Maintains stable and efficient reactor operation, requiring high reliability and corrosion resistance.
- Industrial Boiler Systems: Widely used in industries such as chemical, petroleum, and steel, improving boiler energy efficiency and lowering operational costs.
6. LP Feedwater Heaters Advantages and Challenges
- Advantages
- Increases boiler thermal efficiency, reducing fuel consumption.
- Reduces thermal stress on the boiler and pipes, extending equipment lifespan.
- Enhances combustion efficiency, reducing harmful emissions.
- Challenges
- Requires regular maintenance and cleaning to prevent scaling and corrosion.
- Initial equipment and installation costs are high, necessitating long-term benefit returns.
Low-pressure feedwater heaters are devices used in power and industrial boiler systems that utilize steam extracted from steam turbines to preheat the feedwater entering the boiler. This process enhances the overall thermal efficiency and performance of the system. Low-Pressure Feedwater Heaters (LP Feedwater Heaters) are essential components in power generation and industrial boiler systems. They are designed to use extracted steam from steam turbines to preheat the feedwater before it enters the boiler. This preheating process enhances the overall thermal efficiency of the system, reduces fuel consumption, and minimizes thermal stress on the boiler and associated piping.