Single metal finned tube and bimetal finned tubes
Single-metal finned tubes are made from a single type of metal, such as aluminum or copper, suitable for general heat exchange applications, whereas bimetallic finned tubes are composed of two different metals, such as copper-aluminum composites, each with distinct thermal expansion coefficients, better withstanding temperature changes and reducing stress between the fins and tube walls, while also leveraging the advantages of both metals to enhance overall thermal conductivity efficiency, making them more suitable for high-temperature, high-pressure, or rapidly changing temperature environments.
1. Single Metal VS Bimetal Finned Tubes in Structure and Manufacturing Process:
- Single-metal finned tube: Typically formed by extrusion or rolling, where the tube and fins are integrated into one piece. This manufacturing process is relatively simple, resulting in lower costs.
- Dual-metal finned tube: Consists of two layers of different metals. The inner layer is usually made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or carbon steel, while the outer fins are made of metals with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper. Manufacturing involves separately producing the inner tube and outer fins, then bonding them together through a composite process, which requires higher technical expertise and production costs.
2. Single Metal VS Bimetal Finned Tubes in Material Selection:
- Single-metal finned tube: Often made of aluminum alloy or copper alloy, known for their good thermal conductivity and formability.
- Dual-metal finned tube: The inner tube typically uses corrosion-resistant materials, while the outer fins are selected for their good thermal conductivity.
3. Single Metal VS Bimetal Finned Tubes in Heat Transfer Performance:
- Single-metal finned tube: Consistent and efficient heat transfer due to the uniform material composition.
- Dual-metal finned tube: Despite the different materials of the inner and outer layers, optimized design can achieve high heat transfer efficiency. The inner layers material can be optimized for corrosion resistance, while the outer fins ensure good thermal conductivity.
4. Single Metal VS Bimetal Finned Tubes in Corrosion Resistance:
- Single-metal finned tube: Limited corrosion resistance in certain corrosive environments due to the uniform material composition.
- Dual-metal finned tube: The use of corrosion-resistant materials for the inner layer enhances overall corrosion resistance, suitable for harsher working environments.
5. Single Metal VS Bimetal Finned Tubes in Applications:
- Single-metal finned tube: Suitable for general heat exchanger applications such as air conditioning and cooling systems, especially in cost-sensitive situations.
- Dual-metal finned tube: Due to superior corrosion resistance, often used in chemical, marine, and other environments with high corrosion requirements, as well as applications demanding higher heat transfer performance.
6. Single Metal VS Bimetal Finned Tubes in Cost and Cost-Effectiveness:
- Single-metal finned tube: Lower manufacturing costs, suitable for mass production and cost-sensitive applications.
- Dual-metal finned tube: Higher manufacturing costs, but considering its superior corrosion resistance and heat transfer performance, it can offer higher cost-effectiveness in certain special environments.
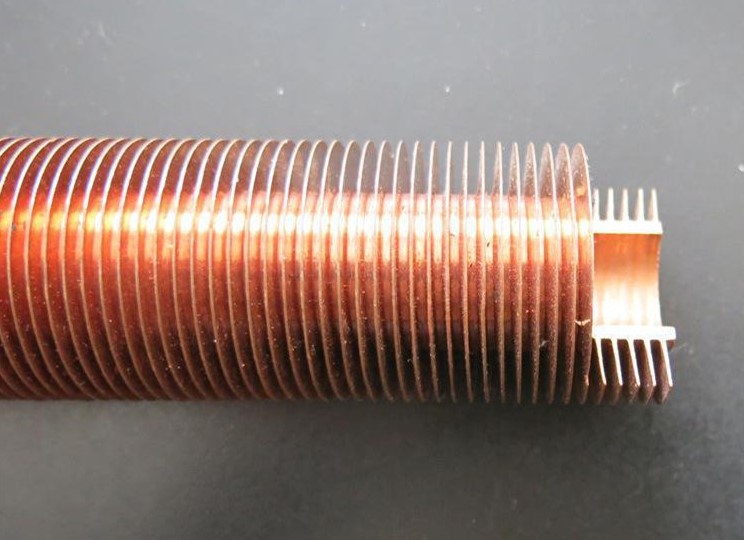
Copper finned tube

