Lord Fin Tube--Single metal finned tube
What Are Single Metal Finned Tubes?
Single metal finned tubes are specialized heat transfer components manufactured by shaping plain tubes into efficient heat exchange surfaces. These tubes feature integrally formed fins that significantly increase the surface area available for heat transfer, making them ideal for applications requiring compact, highly efficient, and stable heat exchangers.
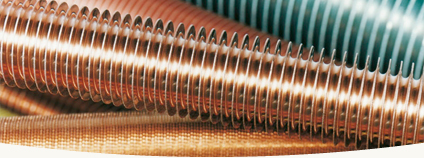
The manufacturing process involves cold rotary extrusion of base tubes made from materials such as aluminum, copper alloys, carbon steel, or stainless steel. This process creates fins with diameters significantly larger than the original tube, resulting in optimal heat transfer efficiency and exceptional durability.
Key Insight: Single metal finned tubes offer superior thermal performance compared to plain tubes, with heat transfer coefficients typically 2-4 times higher depending on fin geometry and application parameters.
Single Metal Finned Tubes Manufacturing Process and Technical Specifications
The production of single metal finned tubes utilizes advanced cold forming techniques that create a permanent, integral bond between the fins and base tube. This process eliminates the thermal resistance typically found in attached fin designs, resulting in superior heat transfer performance.
Manufacturing Methods
- Cold Rotary Extrusion: The most common method where a thick-walled tube is extruded through specialized dies to form fins
- Winding Process: For certain materials, fins are formed by winding ribbon-like material around the base tube under mechanical tension
- Integral Fin Formation: The base tube material itself is shaped to create the fins, ensuring a seamless connection
Single Metal Finned Tubes Performance Characteristics and Advantages
Features
- Compact fin spacing (0.5-2.11mm) providing high surface area density
- Fin thickness typically ranges from 0.2-0.5mm
- Relatively small unit heat transfer area with minimal contact resistance
- Uniform fin formation with bottom folds that act as external air spoilers, enhancing heat transfer
- Material flexibility allowing selection based on durability and formability requirements
Performance Data
| Parameter | Single Metal Finned Tube | Plain Tube | Bimetal Finned Tube |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Coefficient (W/m²K) | 45-120 | 15-40 | 40-100 |
| Surface Area Increase Ratio | 2.5-7.0 | 1.0 | 2.0-6.0 |
| Pressure Drop (Pa/m) | 150-600 | 50-200 | 120-500 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Material Dependent | Material Dependent | Enhanced (liner protection) |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -200 to +400 | -200 to +400 | -200 to +350 |
| Typical Applications | HVAC, Refrigeration, Process Heating | Basic Heat Exchange | Corrosive Environments, High Pressure |
Single Metal Finned Tubes Material
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Corrosion Resistance | Cost Factor | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 205-250 | Good (except in alkaline environments) | 1.0 | HVAC, refrigeration, air cooling |
| Copper Alloys | 380-400 | Excellent (especially seawater) | 2.5-3.5 | Marine applications, power generation |
| Carbon Steel | 45-55 | Poor (requires coating/protection) | 0.7-0.9 | High temperature applications, economizers |
| Stainless Steel | 15-25 | Excellent | 3.0-5.0 | Chemical processing, food industry |
Technical Note: While single metal finned tubes offer excellent thermal performance, the base tube remains partially exposed to the environment, which may require additional corrosion protection in aggressive operating conditions.
Single Metal Finned Tubes Design Considerations and Limitations
Advantages
- Elimination of contact resistance between fin and tube
- Superior mechanical strength and durability
- Excellent thermal performance with high heat transfer coefficients
- Wide range of material options for specific application requirements
- Compact design allowing for space-efficient heat exchanger layouts
Limitations and Challenges
- Fin spacing can lead to fouling accumulation in certain environments
- Condensate and dust removal can be challenging with tight fin spacing
- Base tube exposure to environment may increase corrosion risk
- Manufacturing complexity increases with smaller fin spacing
- Material selection limitations based on formability requirements
Single Metal Finned Tubes Applications Industries
Maintenance and Operational
Proper maintenance is essential for maximizing the service life and performance of single metal finned tubes in heat exchanger applications:
- Regular inspection for fouling and corrosion, particularly in the fin folds
- Appropriate cleaning methods based on application (chemical, mechanical, or hydraulic)
- Monitoring pressure drop increases as an indicator of fouling
- Consideration of protective coatings in corrosive environments
- Periodic performance testing to detect efficiency degradation
Expert Tip: For applications with high fouling potential, consider slightly larger fin spacing (≥2.0mm) to facilitate easier cleaning and maintenance while maintaining excellent thermal performance.

