Tube and Fin vs. Bar and Plate Heat Exchangers
2024-12-21Leave a message
Tube and Fin vs. Bar and Plate Heat Exchangers, Both tube and fin and bar and plate heat exchangers are widely used in thermal systems, but they differ in design, efficiency, and application.
1. Design and Structure comparison
►Tube and Fin: Features tubes with fins wrapped around them, providing a bulkier, larger design. Its ideal for applications where space is less of a concern.
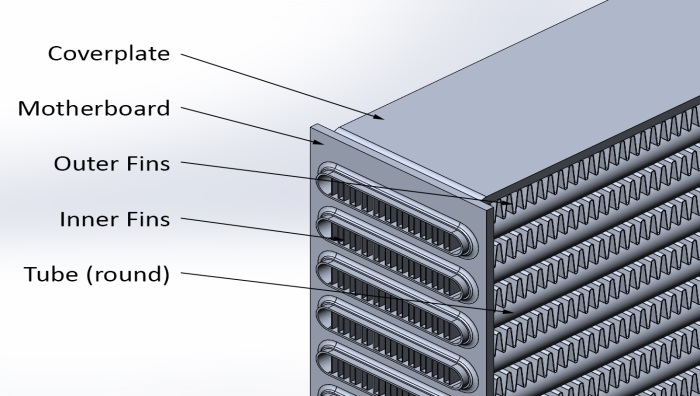
Tube and Fin Heat Exchanger:Involves tubes through which a fluid (usually liquid or gas) flows. Fins are attached around these tubes to increase the surface area for heat exchange.
Fins are typically made of metal, such as aluminum or copper, and are designed to dissipate heat efficiently.
These are often used in large, industrial heat exchangers, air coolers, and radiators.
►Bar and Plate: Composed of stacked plates with alternating air and fluid channels, creating a compact, efficient design that is ideal for space-limited applications.
Bar and Plate Heat Exchanger: Consists of a series of flat plates (often aluminum or stainless steel) stacked together with alternating fluid and air channels.
Each plate is typically brazed or welded together to create a compact structure with very efficient heat transfer.
Often found in automotive and compact heat exchange applications, as well as HVAC systems.
2. Heat Transfer Efficiency comparison
►Tube and Fin: Offers moderate heat transfer efficiency. The larger size allows for more surface area, but it’s less efficient than bar and plate designs.
The heat transfer efficiency depends heavily on the contact surface area between the fin and the fluid. The design is generally optimized to balance between space, cost, and heat transfer.
These systems often work well in applications where the fluid velocity is high, and the heat load is moderate to high, but they may not achieve the same heat transfer efficiency as bar and plate heat exchangers in more compact setups.
►Bar and Plate: Provides higher heat transfer efficiency due to the direct contact between fluid and plate surfaces, making it ideal for performance-focused applications.
Bar and plate exchangers generally have higher heat transfer efficiency due to the smaller, more organized flow channels that allow for greater surface area contact between fluids and the heat exchange surface.
The compact design and direct fluid-to-plate contact make it better suited for high-efficiency applications with limited space.
3. Durability and Maintenance comparison
►Tube and Fin: Less durable, as fins can bend or clog, requiring regular maintenance and repairs.
►Bar and Plate: More durable and resistant to physical damage, with less maintenance required due to its brazed or welded construction.
4. Cost comparison
►Tube and Fin: Lower cost due to simpler design, making it ideal for larger, more affordable systems.
►Bar and Plate: Higher cost because of complex design and materials, but its superior efficiency justifies the price in high-performance applications.
5. Airflow and Pressure Drop comparison
►Tube and Fin: Less restrictive airflow, making it suitable for applications where maintaining engine power and throttle response is important.
►Bar and Plate: Higher pressure drop due to the dense design, which may reduce engine performance if not optimized for airflow.
6. Applications comparison
►Tube and Fin:
Best for larger, budget-conscious systems, such as in general automotive applications, industrial cooling, or street-driven vehicles where space and cooling demands are moderate.
Commonly used in larger systems like radiators, air coolers, automotive radiators, and industrial heat exchangers.
Suitable for low to moderate-pressure applications and environments with variable temperature ranges.
►Bar and Plate:
Ideal for high-performance applications like motorsports, race cars, and high-boost systems, where maximum cooling efficiency and compactness are critical.
Widely used in automotive cooling systems (e.g., intercoolers, oil coolers), HVAC systems, and small heat exchange units.
Perfect for high-performance applications where efficiency and compactness are crucial.
7. Performance compariso
►Tube and Fin: Suitable for moderate cooling needs and longer-distance driving. It’s better for general-purpose use but less efficient in extreme heat scenarios.
►Bar and Plate: Provides superior cooling performance in high-boost or high-heat environments, making it perfect for high-performance setups that demand reliable, efficient heat dissipation.
- Tube and Fin exchangers are cost-effective and good for larger applications with moderate cooling requirements. They excel in situations where space isnt an issue and where performance is not the highest priority.
- Bar and Plate exchangers are more efficient and durable, suited for high-performance and space-limited environments. They are ideal when maximum cooling efficiency and durability are essential, especially in motorsports or high-boost systems.