What is boiler header? & function
What is a boiler header?
The boiler header is also called a header, not an independent component of the boiler. It is composed of water-cooled walls, economizers, and superheaters. In order to improve boiler efficiency, drum boilers have gradually developed into tubular boilers to increase the heat transfer area. The boiler water flows from the drum through the downcomer into the box below, and is distributed to each tube bundle by the box. The water in these tube bundles continuously absorbs heat energy, gathers in the box above, and then flows back into the drum.
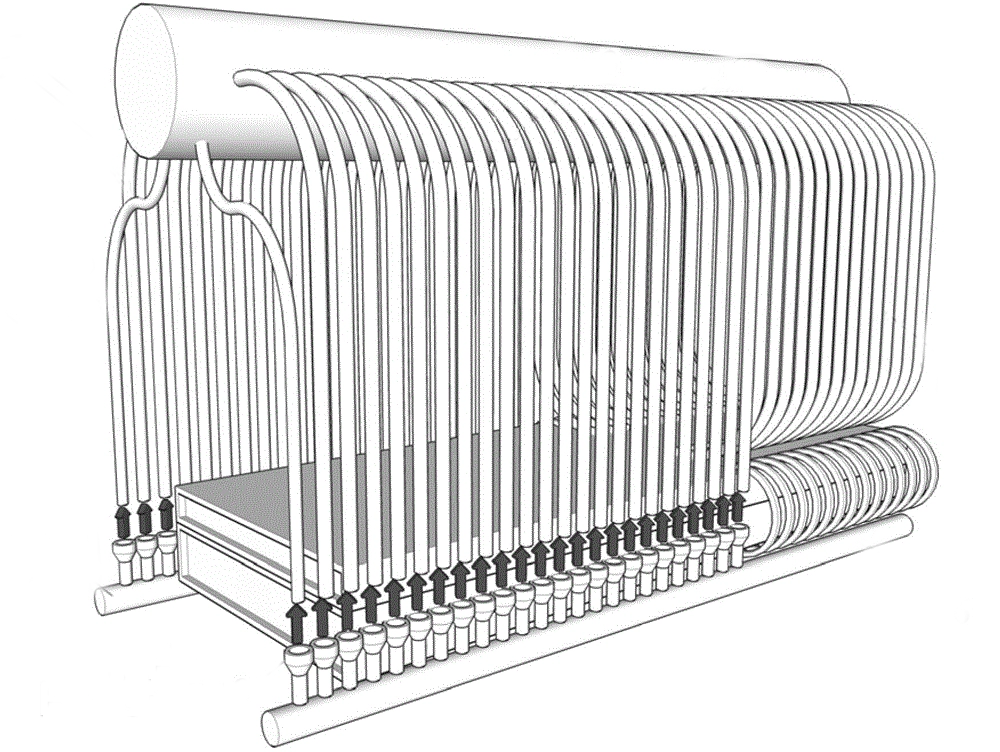
We call the upper and lower boxes headers or headers. The header (also called header) is an important part of the boiler and is divided into upper header and lower header. The lower header is also called the "anti-coking box"
Why is the header called an "anti-coking box"?
The lower header of the boiler also has the function of preventing coking. It is located on both sides of the grate, in direct contact with the burning coal layer, and becomes the main heat-absorbing surface at the bottom of the furnace.
Purpose: To absorb part of the heat, adjust the temperature of the fuel layer, prevent coking, and cool the coked slag so that it does not stick to the side walls, so it is also called an anti-coking box.
Boiler header function:
►1. The function of the boiler header is to collect the working fluid or redistribute the working fluid to other pipes through the header, that is, to collect, mix and distribute the working fluid to ensure uniform distribution and uniform heating of the working fluid. Collecting or distributing steam and water working fluid can reduce the number of working fluid transportation and connecting pipes and the number of openings in the boiler drum, which can improve the safety of the boiler drum.
►2. The header is a pipe fitting for mixing boiler working fluids and ensuring uniform heating of the working fluids. Usually, the furnace wall of an industrial boiler is composed of rows of pipes (water-cooled walls) spliced together, but the boiler is large in size and complex in structure, and it cannot be guaranteed that the working fluids in all pipes have the same heat absorption. The heat absorption of different parts varies greatly. Installing a header allows the working fluids in each pipe to converge here and then distribute them to each pipe at the next level. This can reduce thermal deviation, optimize the heat absorption, flow of the working fluid, cooling of the boiler, and thermal efficiency of the boiler.
►3. The specifications, quantity and arrangement of the pipes in the upper, middle and lower parts of the boiler are different. The header is responsible for connecting the sections to ensure smooth flow of the working fluid.
►4. A lot of heating surface pipes are connected to the boiler header, and they are large diameter pipes, generally made of seamless steel pipes, with flat heads or end covers welded at both ends. Many holes are opened on the box body for welding or expanding pipes. Both ends of the economizer and superheater pipes are connected to the header, the lower end of the water-cooled wall pipe is connected to the header, and the upper end can be connected to the header, and then a few pipes (steam-water outlet pipes) are led out from the header to the boiler drum; the upper end of the water-cooled wall pipe can also be directly connected to the boiler drum.
Boiler header classification:
►1. According to their location, there are upper headers and lower headers or import headers and export headers.
►2. According to the type of tube bundles collected, it is divided into water-cooled wall headers, superheater headers, economizer headers, etc.
Boiler Header structure:
In boilers of various models or grades, the structure of the header is basically similar.
It consists of parts such as the cylinder, end cover, large and small pipe joints, tees, elbows, accessories (pre-welded parts or lifting ears), etc.
Dimensions of boiler header:
The diameter of the header in a power station boiler is generally in the range of φ89mm to φ914mm.
The wall thickness ranges from 7mm to 150mm and the maximum length is about 23000mm.
Material: Carbon steel (such as 20G, SA-106B, SA-106C), low alloy heat-resistant steel (such as 15CrMoG, 12Cr1MoVG, WB36, SA-335P12, SA335-P22), medium alloy heat-resistant steel (such as SA-335P91), and SA-335P122 and SA-335P92 are used in ultra-supercritical boilers.
The equipment commonly used in header manufacturing generally includes beveling machines, drilling machines, boring machines, automatic submerged arc welding machines for circumferential seams, CO2 gas shielded welding machines, pipe bending machines, hydraulic presses, heat treatment furnaces and plunger-type hydraulic pumps.
Requirements for cleanliness inside the header:
►1. If there are straw hats, iron filings and other debris inside the header, it is very easy to cause pipe explosion and other shutdown accidents when the power plant is running. Therefore, the cleanliness of the inside of the header must be strictly controlled.
►2. After drilling the holes in the header, use the inner R wind milling cutter to clean the straw hats and burrs on the inner wall of the pipe hole, and clean up the debris inside the header in time. Try to avoid dropping debris into the header during welding. When chamfering after water pressure, cover other pipe joints to prevent iron filings from falling in.
►3. During the final cleaning before leaving the factory, each pipe joint is checked through a wire rope to prevent foreign objects from blocking the pipe joint. Compressed air is used to blow the inside of the barrel to clean up the debris. Finally, an endoscope is used to check each pipe joint and the inside of the header to ensure that the internal cleanliness of each header leaving the factory meets the requirements.
Boiler Header Application areas:
►1.The main purpose of high-pressure boiler tubes is as a transmission pipeline under high temperature and high pressure environment, used for superheated steam pipes of high-pressure or ultra-high pressure boilers, heat exchangers and pipes for high-pressure equipment. The working pressure is generally above 9.8Mpa and the working temperature is between 450℃ and 650℃.
►2.In the energy field, it is used to build boiler systems in thermal power plants to transport high-temperature and high-pressure steam and hot water to ensure the normal operation of generators.
►3.In the chemical industry, high-pressure boiler tubes are used to transport various corrosive media, such as acids, alkalis, salts, etc.

