Introduce Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tubes for High‑Pressure Boiler Systems
Internally multi‑lead rifled (MLR) steel tubes are specialized cold‑drawn or cold‑rolled seamless tubes with a helical rib structure on the inner surface. This design ensures stable nucleate boiling under extreme thermal loads, preventing film boiling and the associated tube wall overheating. As a result, these tubes significantly extend boiler service life in demanding power‑generation applications.
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Applications
These tubes are engineered for the most critical heat‑transfer sections of modern power stations:
- Water‑cooled wall systems in large‑capacity utility boilers
- Supercritical and ultra‑supercritical pressure boilers
- High‑pressure heat exchangers and economizers
- Once‑through boiler designs where reliable coolant contact is essential
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Function
The internal helical ribs create a controlled rotational flow in the working fluid. This action increases turbulence near the tube wall, sweeping steam bubbles away and forcing water to maintain contact with the metal surface. By preventing the formation of an insulating steam film, the Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube delays the onset of heat‑transfer deterioration, ensuring efficient cooling even at high heat fluxes.
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Materials
Manufactured from seamless boiler‑grade steels, common material specifications include:
- ASTM A106 Gr. B (carbon steel)
- ASTM A210 Gr. A1 & Gr. C (medium‑carbon)
- ASTM A213 T2, T11, T12, T22, T23 (chromium‑molybdenum alloys)
Material selection depends on operating temperature, pressure, and corrosion environment. All materials undergo strict decarburization checks to ensure surface integrity.
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Classifications
Two primary design types, A and B, are defined by geometric parameters. The table below outlines the key dimensional differences.
| Type | Lead Angle | Rib Side Angle | Rib Width at Top (Longitudinal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 30° | 55° | 8.28 mm |
| B | 30° | 50° | 5.59 mm |
The choice between Type A and B depends on the specific boiler design and desired fluid dynamics. Type A, with a wider rib top, offers a larger heat‑transfer surface, while Type B promotes slightly different flow characteristics.
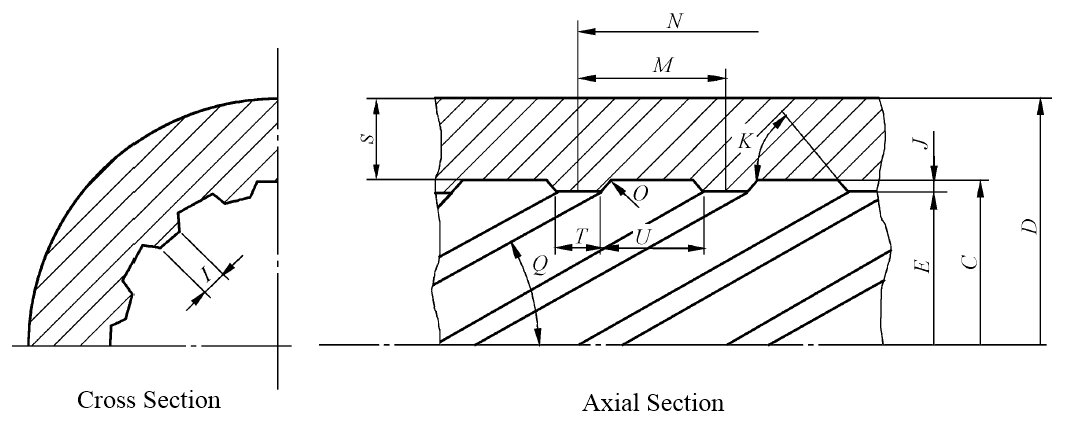
Dimensional display of a multi‑lead rifled tube showing key parameters.
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Dimensions
Standard production ranges cover the needs of most boiler designs:
- Tube Outer Diameter (OD): 28.58 mm – 76.2 mm
- Tube Length: 8,000 mm – 12,000 mm (longer lengths available upon request)
- Wall Thickness: As per ASME or EN specifications, typically from 3.0 mm upwards
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Tolerances
Precise manufacturing ensures consistent performance. Critical tolerance ranges are summarized below.
| Parameter | OD Range (mm) | Tolerance Type A (mm) | Tolerance Type B (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tube Outer Diameter (D) | OD ≤ 38.1 | ±0.15 | ±0.15 |
| 38.1 < OD < 50.8 | ±0.20 | ±0.20 | |
| 50.8 ≤ OD < 63.5 | ±0.25 | ±0.25 | |
| OD ≥ 63.5 | ±0.30 | ±0.30 | |
| Rib Height (J) | OD ≤ 38.1 | ±0.20 | ±0.18 |
| Minimum Wall Thickness (Smin) | All | +22% | +22% |
| Straightness | All | ≤ 1.0 mm per meter | |
Additional geometric controls include ovality (≤80% of OD tolerance) and eccentricity (≤80% of wall thickness tolerance).
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Testing
Each production batch undergoes rigorous quality verification.
- Flattening Test: Verifies ductility; no delamination or cracks allowed.
- Flaring Test: Performed with a 60° cone mandrel to specified expansion.
- Hydrostatic Test: Every tube is tested (max pressure 20 MPa) with no leakage.
- Non‑destructive Examination: Full‑length ultrasonic inspection for material integrity.
- Decarburization Inspection: Surface decarb depth strictly limited per ASTM standards.
Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube Weight Calculation
The theoretical weight per meter accounts for the added volume of the internal ribs. The formula is:
Z = [π × (D - S) × S + G × J × (I + (tan Q / tan K) × J)] × ρ / 1000
Where Z is weight (kg/m), D is OD (mm), S is wall thickness (mm), G is number of ribs, J is rib height, I is rib top width (circumferential), Q is lead angle, K is rib side angle, and ρ is material density (kg/dm³).
Multi Lead Rifled versus Smooth Tubes
The transition from smooth‑bore to rifled design represents a significant advancement in boiler technology. The comparative benefits are clear.
| Parameter | Smooth Boiler Tube | Multi‑Lead Rifled Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Standard, prone to film boiling at high flux | Enhanced, maintains nucleate boiling longer |
| Flow Characteristics | Linear, less turbulence | Helical, induced swirl improves mixing |
| Critical Heat Flux | Lower threshold | Significantly higher threshold |
| Tube Wall Temperature | Higher risk of hotspots | More uniform, reduced thermal stress |
| Application | General‑duty boilers | High‑pressure, high‑capacity utility boilers |
This comparison underscores why Multi Lead Rifled Steel Tube technology is the preferred choice for modern, efficient, and reliable power‑generation systems. The internal ribbing directly addresses the primary failure modes of boiler tubes, offering plant operators greater safety margins and longer maintenance intervals.
For procurement teams, specifying MLR tubes requires attention to the boiler manufacturers design drawings, the correct tube type (A or B), material grade, and the complete set of testing certifications. Partnering with a manufacturer experienced in cold‑drawing rifled profiles ensures geometric consistency and metallurgical quality, which are vital for trouble‑free installation and decades of service.

