Products Description
A pressure vessel is a container, typically used to store gas or liquid, that is specifically made to withstand internal or external pressure. The petroleum, chemical, energy, food, and pharmaceutical industries all make extensive use of it. Because pressure vessels must be able to bear high pressure, their design and construction must closely adhere to all applicable regulations and requirements to guarantee their dependability and safety. A pressure vessels structure typically consists of the main body, head, flange, nozzle, and support. Of these, the head is a crucial part that has a direct impact on the containers overall strength and sealing ability.
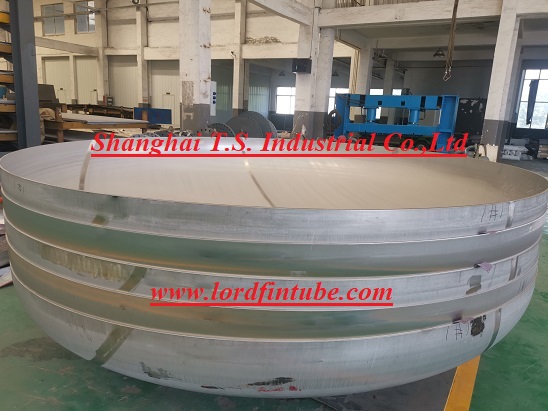
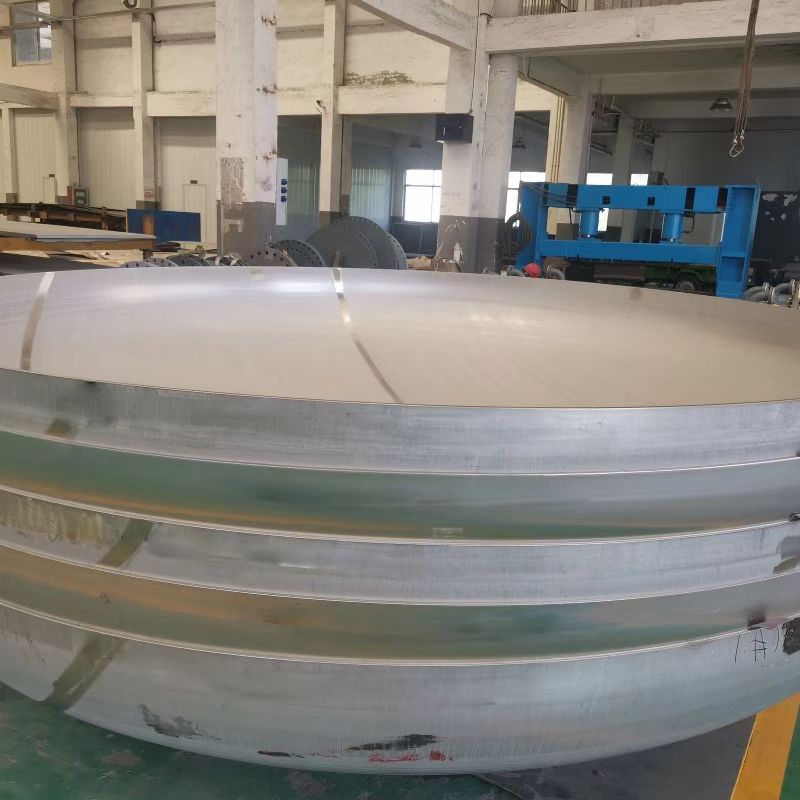
One part used to seal a pressure vessels end is the head, also known as the end cap. In order to sustain internal or external pressure loads, it is typically utilized at both ends of a pressure vessel. In order to guarantee that the medium within the container does not leak and to keep outside materials out, the end cap is typically welded to the container body.
Functions of Vessel Heads:
✔ To close container, providing good sealing
✔ To withstand internal and external pressure
✔ To strengthen structural strength
Available Materials for Head:
Single material: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, titanium alloy, etc.
Composite materials
OD: 300mm-6000mm
WT: 3mm-40mm
Typical Boiler Head Type:
Based on their shapes, manufacturing methods, and relevant situations, pressure vessel heads can be categorized into the following common types:
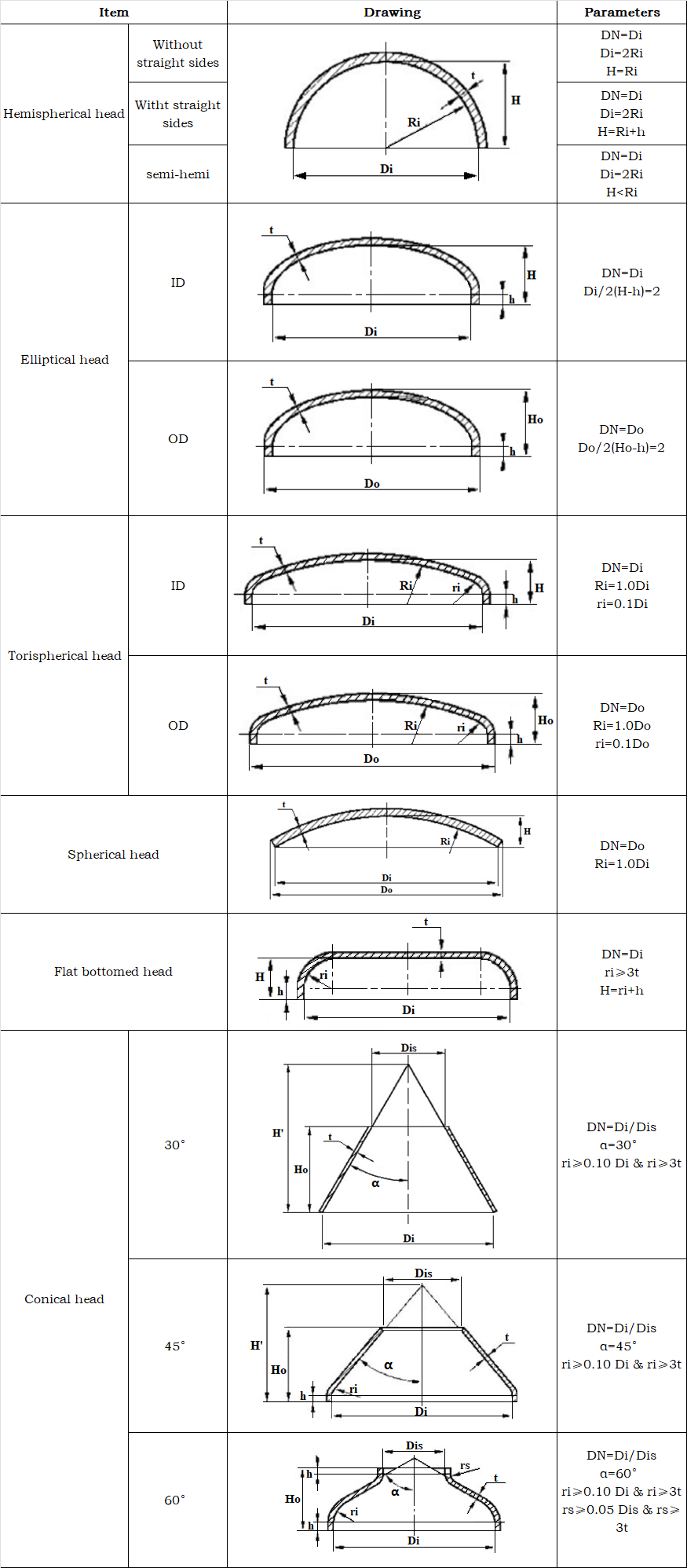
Paremeters
- Di: inside diameter
- Do: outside diameter
- Ri & rs: radius
- H: inside height
- Ho: outside height
- t: thickness
⚑ Hemispherical head
The head is made up of a straight edge (cylinder short section) and a half-spherical shell. The force is constant, and the spherical surfaces radius of curvature is the same everywhere.
When exposed to the same internal pressure as the other heads, the hemispherical head needs the thinnest wall. The edge stress brought on by the change in the radius of curvature at the junction of the spherical shell and the cylinder of the same thickness is only 3.1% of the cylinders total film stress, meaning it can be disregarded. Consequently, the hemispherical head has the most cost-effective materials and the highest mechanical qualities.
✔ Disadvantages: The overall stamping is difficult when the depth is large and the diameter is small. The large diameter uses split stamping, and the welding workload is also large.
✔ Application: high-pressure vessels
⚑ Elliptical head
It is composed of a cylindrical straight segment and a revolving ellipsoidal sphere. Its mechanical qualities are superior to those of the butterfly head, but second only to the hemispherical head.
The stress distribution is quite uniform due to the ellipsoidal parts smooth and continuous change in meridian curvature, and the ellipsoidal heads depth is significantly less than that of the hemispherical head, making it easier to stamp.
✔ Role of the straight edge:
To guarantee the heads manufacturing quality and prevent edge stress from being applied to the circumferential weld between the cylinder and the head.
✔ Application: medium and low pressure vessels
⚑ Torispherical head
It is made up of a transition section, a cylindrical straight edge, and a spherical surface. It is straightforward to make and has a comparatively basic structure. However, the edge stress is significantly higher than the film stress brought on by the inner ash, and the mechanical properties are marginally worse than those of the elliptical head because of the abrupt change in the radius of curvature at the junction of the folded edge and the straight edge and the spherical shell.
✔ Application: Only utilized when there is a shortage of molds or when low pressure necessitates reducing the head depth.
⚑ Spherical head
To create a spherical cap head, the spherical portion of the dished head is welded directly to the cylinder after the transition and straight edge are removed.
✔ Function: Usually employed as the intermediate head of two separate pressure-bearing containers, the spherical cap head can also serve as the containers end cover.
⚑ Flat bottomed head
Among various heads, the flat plate has the simplest structure and is the most convenient to manufacture, but it requires the largest thickness under the same diameter and pressure.
Compared with spherical and elliptical heads, its pressure-bearing capacity is poor.
✔ Application: Only used for small-diameter and low-pressure containers
⚑ Conical head
The shell surface is conical, which helps guide the fluid.
✔ Application: Mostly used for the bottom cover of chemical equipment
✔ Advantages: It is easy to collect and remove solid materials in the equipment.
Pressure Vessel Heads
How to choose the type of head?
1. Geometry
-The surface area per unit volume is the smallest for hemispherical heads.
-The volume and surface area of elliptical and dished heads are the same
2. Mechanics
-The stress distribution of hemispherical heads is the best
-The stress situation of elliptical heads is second
-The biggest disadvantage of dished heads in mechanics is that they have a small folding radius r
-The stress situation of flat-bottomed heads is the worst
3. Manufacturing difficulty
The deeper the head, the larger the diameter and thickness, the more difficult it is to manufacture
Manufacturing Process of Pressure Vessel Heads
- Raw materials: sheet or composite plate
- Process: stamping, spinning, rolling, split molding
Applications of Pressure Vessel Heads
- Oil and gas storage
- Chemical storage and handling
- Reactor