The structure of shell and tube heat exchangers and Main parts
2024-04-23Leave a message
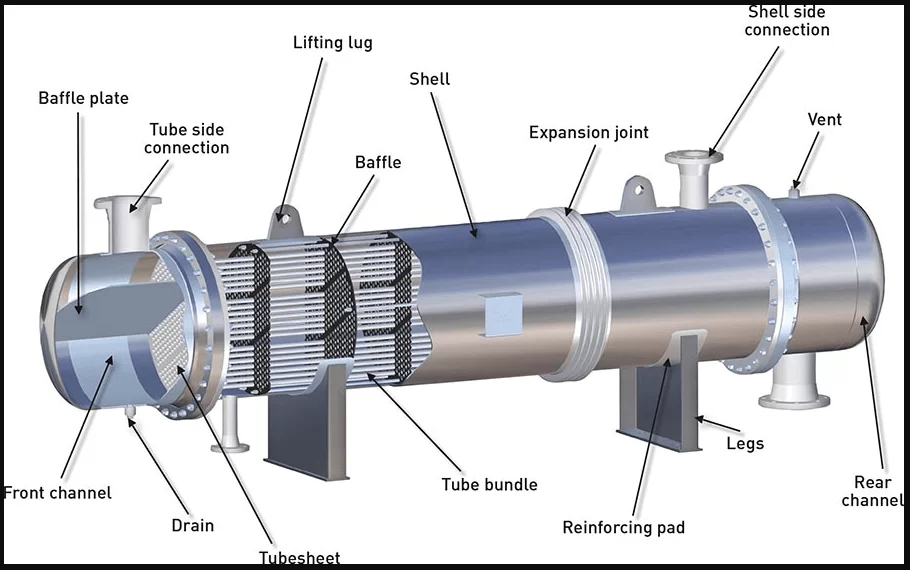
Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a cylindrical shell enclosing a bundle of tubes, with key components including baffles, tube sheets, connections for fluid inlet and outlet, and support structures.
1. What is Shell?:
The shell serves as the outer housing of the heat exchanger. It contains one of the fluid streams and is typically constructed from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or other alloys depending on the application and operating conditions.
2. What is Tube Bundle:
The tube bundle is the core component of the heat exchanger where heat transfer occurs. It consists of a series of tubes through which one fluid flows while the other fluid flows around the outside of the tubes. The tubes can be straight or bent, and they are usually made of materials such as copper, stainless steel, or titanium.
3. What is Tubesheet:
The tubesheet is a thick metal plate located at both ends of the tube bundle. It serves to support and secure the tubes in place, providing a leak-proof seal between the tube bundle and the shell.
4. What are Baffles:
Baffles are plates or spacers placed inside the shell to direct the flow of the shell-side fluid. They promote turbulence in the fluid flow, which enhances heat transfer efficiency by increasing the mixing of the fluid. Baffles also help to support the tubes and prevent vibration.
5. What is Baffle Plate:
The baffle plate is a large plate attached to the inner wall of the shell. It supports the baffles and helps to guide the flow of the shell-side fluid through the heat exchanger.
6. What is Front Channel and Rear Channel:
These are the spaces between the baffles where the shell-side fluid flows around the tube bundle. The front channel is located near the inlet of the shell-side fluid, while the rear channel is located near the outlet.
7. What is Tube Side Connection:
These are the inlet and outlet connections for the fluid flowing through the tubes. They allow the tube-side fluid to enter and exit the heat exchanger.
8. What is Shell Side Connection:
These are the inlet and outlet connections for the fluid flowing around the outside of the tubes. They allow the shell-side fluid to enter and exit the heat exchanger.
9. What is Vent:
The vent is an opening on the shell of the heat exchanger used to remove trapped air or gases during startup or operation. It ensures proper operation and prevents air pockets from interfering with heat transfer.
10. What is Drain:
The drain is an opening on the shell or tubesheet used to remove liquid from the heat exchanger. It is typically used for maintenance purposes or for draining the system during shutdowns.
11. What is Expansion Joint:
An expansion joint is a flexible element installed in the shell or tube bundle to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. It prevents damage to the heat exchanger caused by temperature fluctuations.
12. What are Heat Exchanger Legs:
Legs are support structures attached to the bottom of the heat exchanger to elevate it above the ground or other surfaces. They provide stability and facilitate installation and maintenance.
13. Lifting Lug:
Lifting lugs are welded to the shell of the heat exchanger and used for lifting and handling during installation or maintenance.
14. Reinforcing Pad:
Reinforcing pads are additional material welded to the shell or other components to strengthen areas subjected to high stress or pressure, such as nozzle connections.
These components work together to facilitate efficient heat transfer between the two fluid streams while ensuring structural integrity, reliability, and safety of the heat exchanger.