What is Coaxial Heat Exchanger?
2025-07-07Leave a message
What is a Coaxial Tube-in-Tube Heat Exchanger?
A coaxial heat exchanger consists of two concentrically arranged tubes of different diameters, hence also known as a tube-in-tube coaxial heat exchanger. This type of heat exchanger falls under the category of shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Typically, the outer tube serves as the shell, while the inner tube acts as the heat transfer tube. Thus, the flow path inside the inner tube is called the tube side, and the space between the inner and outer tubes is referred to as the shell side.
Structure & Working Principle
Key Components:
- Inner tube
- Outer tube
- Supports
- Fluid inlets/outlets
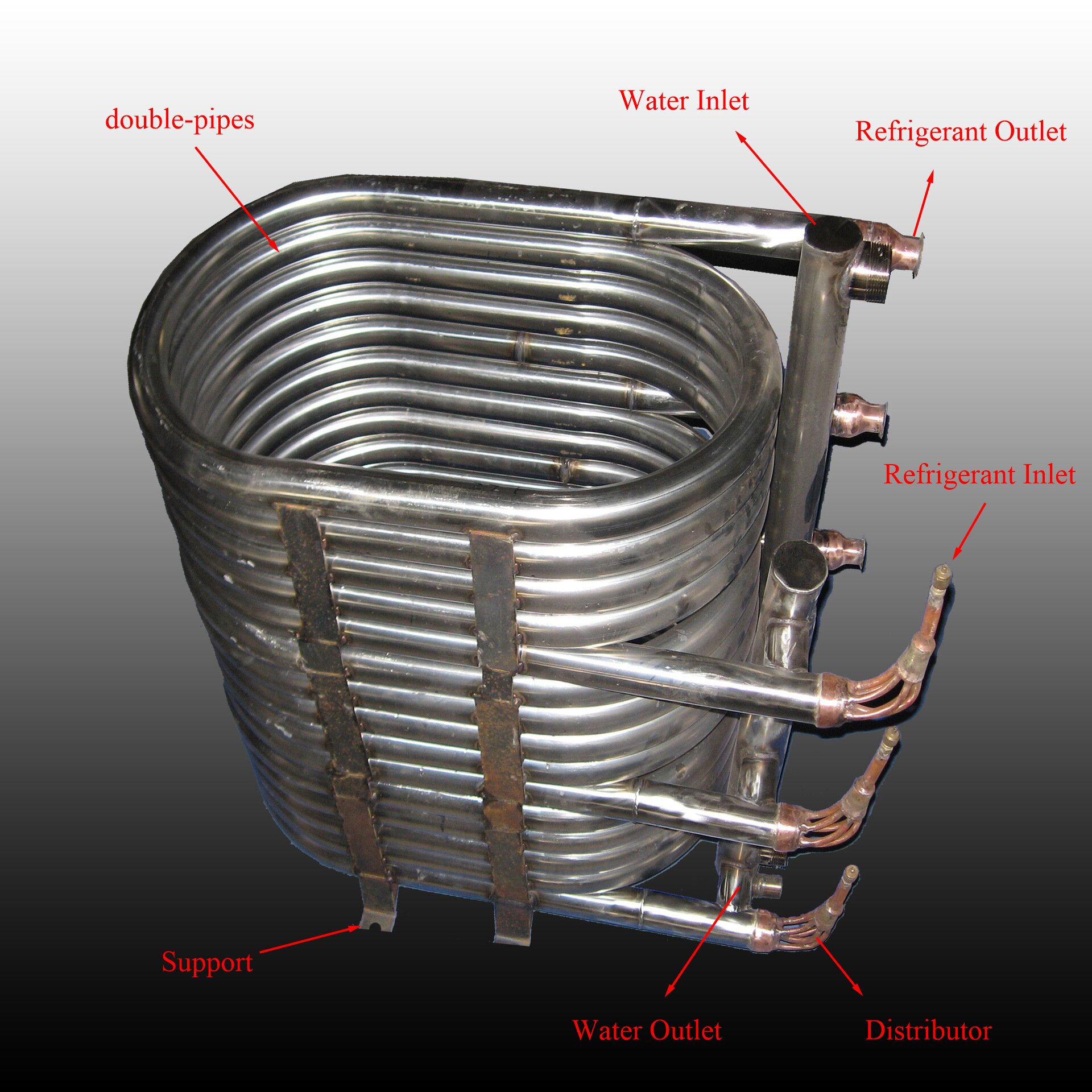
Structure of Coaxial Heat Exchanger
A coaxial heat exchanger generally comprises the above components. The inner tube carries the fluid to be cooled (e.g., hot fluid or secondary refrigerant), while the outer tube conveys the cooling medium or refrigerant.
Heat transfer occurs when the hot fluid in the inner tube releases heat through the tube wall to the cold fluid in the outer tube. Flow is typically counter-current: one fluid enters from one end while the other enters from the opposite end, maximizing the mean temperature difference and thermal efficiency.
Tube Materials & Types
Inner tube materials: Copper, Cupronickel, Titanium, Stainless steel
Outer tube materials: Steel, Copper, Cupronickel, Titanium, Stainless steel
Inner tube types: Spiral-grooved tubes (smooth or enhanced surface) & Multi-tube helical bundles
Outer tube types: Plain tubes + Rust-proof paint
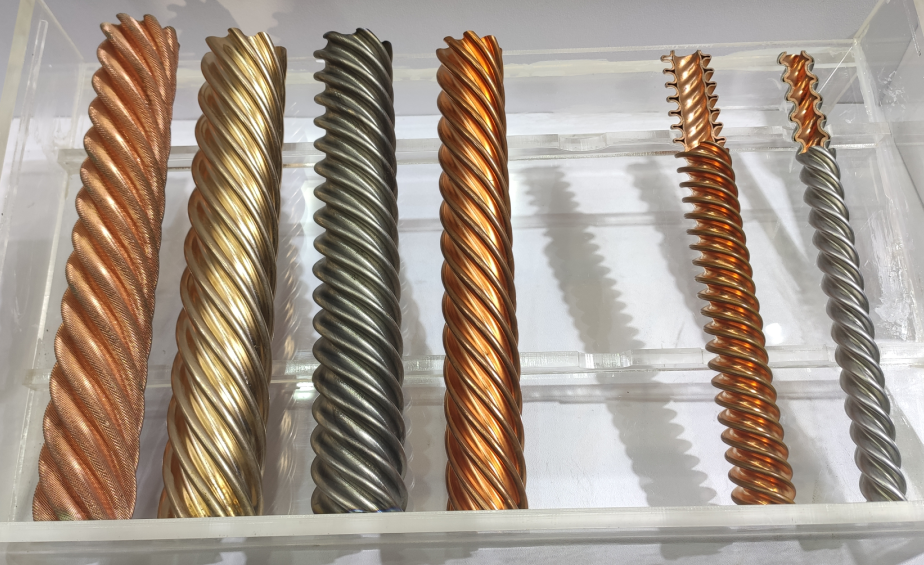

Types of Tube-in-Tube Heat Exchangers
1. By shape:
- Circular
- Square
- U-shaped
- Double-coil
2. By system:
- Single-system
- Multi-system
Product Features of Coaxial Heat Exchanger
Compact & Simple: Minimal components and small footprint; relatively easy to manufacture.
Oil Return Reliability: Absence of vertical upward flow paths in the refrigerant circuit ensures safe oil return to the compressor even at low flow rates. Eliminates risks like oil trapping (reducing heat transfer area), flow blockage, and compressor damage.
Enhanced Heat Transfer: Inner tube features multi-head helical design. The external embossed surface increases heat transfer area, while internal spiral grooves promote turbulence—significantly improving thermal performance. Reduces clogging risk and prevents freezing in winter.
Structural Integrity: The helical coaxial design minimizes weld joints. Simplified welding processes ensure high-quality connections, drastically reducing the risk of leaks or ruptures caused by long-term pressure and vibration.
Main Applications
- Evaporators & condensers for water-source/ground-source heat pumps
- Small/residential heat pump units
- Condensers or subcoolers for chillers/refrigeration units
- Ice machine coolers
- Evaporators for oil cooling units

